2026年1月,全球加密货币市场再次被Cryption ai+ 交易所年度AI机器人大赛点燃
星世纪(NovaEra)NEAI 4.0:让AI成为每个投资人的「智慧副驾驶」
AI智能引擎改写交易规则:Cryption ai+以算法生态系重构全球金融市场
Winter Storm Persists Across the U.S. – MojiWeather Reminds Users to Heed Safety Guidelines
Japanese Anime Captures 60% of Asian Entertainment Revenue While K-Pop’s 150M Global Fans Dominate Music Charts
Coagulation Analyzer Market Insights

[ad_1] Market Overview Market Size and Forecast Key Market Drivers Competitive Landscape Market Segmentation Regional Insights Opportunities for B2B Stakeholders Future Outlook Related Healthcare Reports- Microbiome DNA Kit Market Mitochondrial Disease Therapies Market Morgellons Disease Market Myocardial Infarction Drugs Market
Advanced Infusion System Market Trends

[ad_1] Market Overview Market Size and Forecast Key Market Drivers Competitive Landscape Market Segmentation Regional Insights Market Opportunities for B2B Stakeholders Future Outlook Related Healthcare Reports- Scalp Cooling System Market US Robotics Prosthetics Market SERS Substrate Market Serum Separation Gel
Apoptosis Testing Market Trends & Insights

[ad_1] Market Overview Market Size and Forecast Key Market Drivers Competitive Landscape Market Segmentation Regional Insights Market Opportunities for B2B Stakeholders Future Outlook Related Healthcare Reports- Caspofungin Market Medical Physics Market Melanoma Diagnostics and Therapeutics Market Levofloxacin Market Ligases Enzyme
Arthralgia Management Market Insights

[ad_1] Market Overview Market Size and Forecast Key Market Drivers Competitive Landscape Market Segmentation Regional Insights Market Opportunities for B2B Stakeholders Future Outlook Yersinia Diagnostics Market Uropathy Treatment Market Varicella Vaccine Market VAT Photopolymerization 3D Printing Technology Market Blotting Processor
Antibody Purification Service Market Trends

[ad_1] Market Overview Market Size and Forecast Key Market Drivers Competitive Landscape Market Segmentation Regional Insights Market Opportunities Future Outlook Stretcher Chair Market Sulfonylurea Market Sulphonamide Market Supercritical Fluid Chromatography Market Surgical Case Cart Market Neurofeedback System Market Neonatal and
Atypical Mycobacteriosis Treatment Market Outlook

[ad_1] Market Overview and Industry Landscape Market Size and Growth Outlook Key Market Drivers and Demand Factors Competitive Landscape and Company Positioning Market Segmentation and Commercial Applications Regional Performance and Market Expansion Innovation Trends and Strategic Opportunities Future Outlook for
HDMI Retimer IC Market: Global Market Size, Growth…
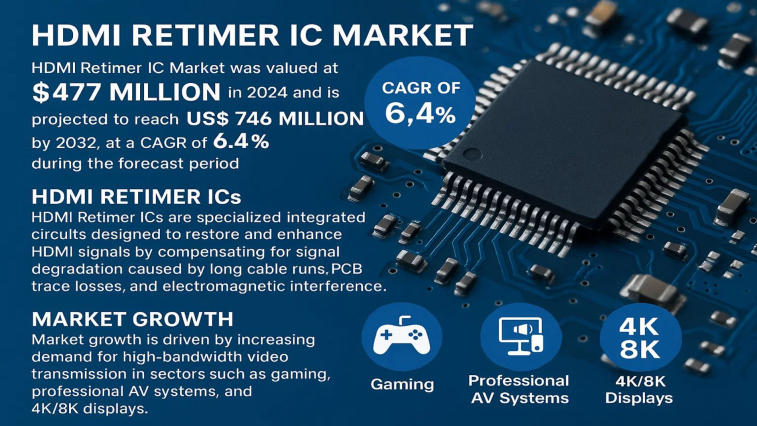
[ad_1] Segment Analysis: By Type PCIe 4.0 PCIe 5.0 PCIe 6.0 Others By Application Servers Storage Devices Hardware Accessories Others By End-User Industry Data Centers Consumer Electronics Telecommunications Industrial Automation Texas Instruments (U.S.) Astera Labs (U.S.) Parade Technologies (Taiwan) Broadcom
What Is the Future of the Neurostimulation Devices…

[ad_1] Rising prevalence of neurological and pain disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, and chronic back pain Technological innovation in implantable systems, such as MRI-compatible and closed-loop devices Growing emphasis on opioid alternatives for pain management Expansion of specialized neuromodulation centers
What Is the Future of the Rechargeable Oral Irriga…
What Is the Future of the Classical Swine Fever Va…

[ad_1] High disease endemicity in major pork-producing countries, especially across Asia-Pacific Government-led vaccination mandates and subsidy programs supporting mass immunization Rising commercial pig farming operations, where biosecurity is critical to profitability Growing recognition of wild boar populations as disease reservoirs,
SQUID Magnetometer Market: Global Market Size, Gro…

[ad_1] Segment Analysis: By Type DC SQUID RF SQUID By Application Healthcare Magnetoencephalography (MEG) Cardiac Imaging Others Industrial Manufacturing Aerospace and Defense Geological Survey Research and Development Others By End User Research Institutions and Universities Hospitals and Diagnostic Centers Industrial
Semiconductor Manufacturing Cables Market: Global …
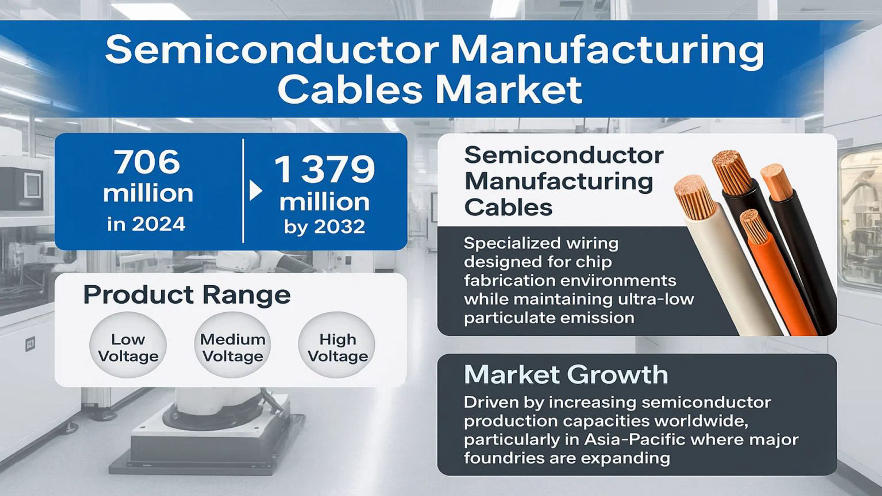
[ad_1] Segment Analysis: By Type Low Voltage Cables Medium Voltage Cables High Voltage Cables By Application Mechanical Equipment and Instrumentation System Information Transmission System Power System By Jacket Material Fluoropolymer-based (PTFE, PFA, FEP) Silicone-based Polyurethane-based Others Helukabel (Germany) Gore (U.S.)
Non-Laser Light Sources for Semiconductor Market: …
Market Report: Acrylates and Dimethicone Copolymer…
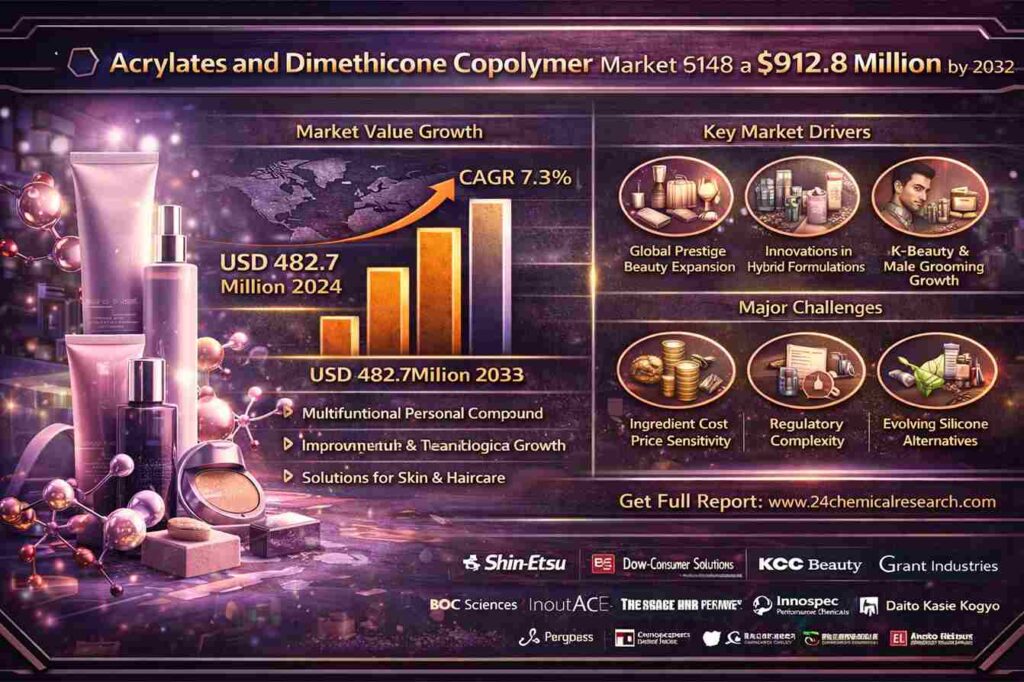
[ad_1] Market Overview & Regional Analysis Key Market Drivers and Opportunities Challenges & Restraints Market Segmentation by Type 98%-99% Purity Above 99% Purity Other Specialty Grades Market Segmentation by Application Hair Care (Conditioners, Styling Products) Color Cosmetics (Foundations, Lip Products)
Detonator Market Set for Strong Expansion, Climbin…

[ad_1] Industrial Electric Detonators Shock Tube Detonators Electronic Detonators Others Coal Mines Metal Mines Non-metal Mines Quarrying and Construction Railway or Road Construction Hydraulic & Hydropower Projects Others Mining Companies Construction Firms Demolition Contractors Government Infrastructure Projects Others Orica Limited






